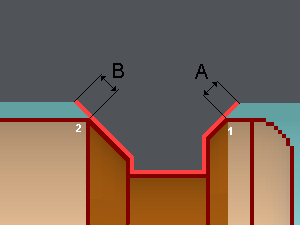
Lead in and Lead out Overlengths, Lead in and Lead out Linear Overlengths
Cycle: Roughing, TurnyuGO, //Roughing, Balanced Roughing, Finish, Finishing B simultaneous, Balanced Finishing, Form Finishing, Direct Grooving, Z Level Grooving, Zig Zag Grooving, W type Grooving, O Ring Type Grooving, Finish Groove
Definition
These functions allow you to define specific overlengths on the toolpath
Lead in overlength (A)
It extends (positive value) or shortens (negative value) the first element of the profile.
The overlength is linear when the first profile element is a segment, circular when it is an arc.
Lead out overlength
It extends (positive value) or shortens (negative value) the last element of the profile.
The overlength is linear when the last profile element is a segment, circular when it is an arc.
Lead in linear overlength (B)
It is a starting distance, always linear and tangent to the first profile element.
Lead out linear overlength
It is an ending distance, always linear and tangent to the last profile element.
You can add overlengths (4th example), the leadin or leadout overlength have priority on start or end linear overlength.
The following examples deal with leadin and lead in linear overlength, the principle is the same for lead out overlengths.
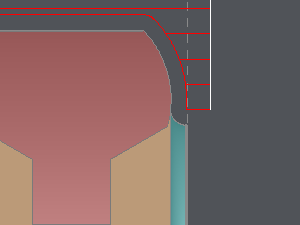
Without any overlength
A: lead in overlength: on circular element | B: lead in linear overlength (tangent on circular element) |
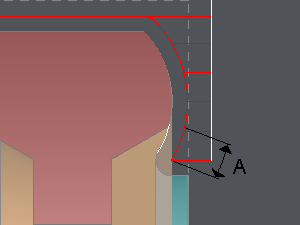 | 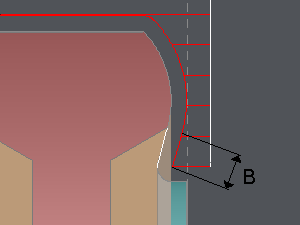 |
with A: lead in overlength and B: lead in linear overlength (if the tool is able to do it).
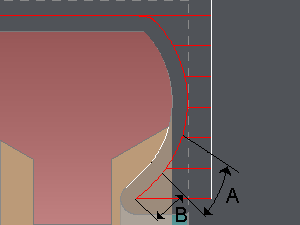
Example for all Grooving cycles.
Lead in linear overlength (A)
It is a starting distance, always linear and tangent to the first profile element and limitated by the stock.
Lead out linear overlength (B)
It is an ending distance, always linear and tangent to the last profile element and limitated by the stock.