Offset Type, Toolpath and Quadrant
This option is used in several machining cycles, with different purposes and behaviours.
Please use the tree on the right side of the screen.
Cycle: Roughing, // Roughing, Balanced roughing, Roughing pass, Finishing / Finishing Ø / Face, Balanced Finishing
Definition
These commands are used to define the pilot points and the calculation of the toolpath.
Offset type for Roughing, // Roughing, Roughing pass, Finishing
It allows to take into account or not of the tool radius compensation.
The pull down menu offers:
Left: The ISO code generates instruction G41.
Center: The ISO code generates instruction G40 (no compensation).
Right: The ISO code generates instruction G42.
This Offset Type is available for Finishing Ø / Face Only.
Offset type for Finishing Ø / Face
It enables to take into account or not of the tool radius compensation.
The pull down menu offers:
With: the ISO code generates instruction G41 or G42, according to the type of toolpath chosen.
Without: no compensation is programmed.
Toolpath
The toolpath is calculated by GO2cam and takes into account or not the tool radius. The pull down menu offers:
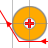 | Part (Tool center): GO2cam does not calculate offset toolpath. The ISO programming follows the geometrical contour. In the case where the tool does not pass, GO2cam recalculates a new appropriate path and manages the collision. |
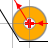 | Tool Center: GO2cam calculates the tool offset toolpath on the right side, according to the Cycle Type (see above). |
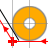 | Imaginary Nose: GO2cam calculates the toolpath and manages collisions. The radius is correctly completed in the GO2cam TOOL panel. The quadrant number is taken into consideration. |
 | Part (Imaginary Nose): GO2cam correctly manages the toolpath in inter cycles and rapid motions and in particular with a tool compensation. |
Part (Tool Center) programming
In this case we must enter the insert radius value in the machine.
Offset type: Left (gives G41)
Right (gives G42)
Toolpath: Part (Tool center)
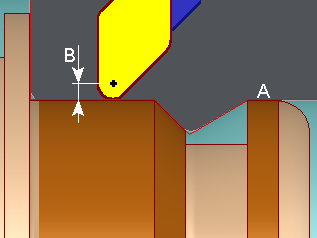
A. Programmed toolpath
B. Insert radius compensation included in CNC.
Tool Center programming
In this case, the insert radius completed in the machine is not taken into consideration.
Offset type: Center
Toolpath: Tool center
GO2cam programs the insert center toolpath on the right side of the part according to the programmed Cycle Type.
If we complete Offset type = Left or Right, GO2cam programs the G41 or G42 compensation. The effect is to generate an additional offset by the machine since the insert radius compensation is taken into consideration.
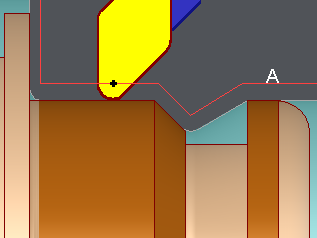
A. Programmed toolpath
Imaginary Nose programming
In this case, the insert radius completed in the machine is not taken into consideration.
The quadrant number must be completed.
Offset type: Not Available
Toolpath: Imaginary Nose
GO2cam programs the Imaginary Nose (fictitious point) toolpath on the right side of the part according to the programmed Cycle Type and the assigned quadrant number.
If we complete Offset type = Left or Right, GO2cam programs the G41 or G42 compensation. The effect is to generate an additional offset by the machine since the insert radius compensation is taken into consideration.
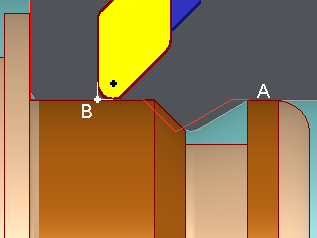 |  |
A. Programmed toolpath
B. Imaginary Nose (i.e n°9 in the quadrant)
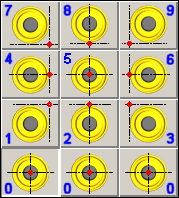
Quadrant(Imaginary Nose No.)
Gives the tool orientation. Is useful only when using Imaginary Nose toolpath.
The numbers correspond to the positions on the PC keyboard. The LATHES quadrant numbers do not inevitably correspond to those of GO2cam. The post-processors updates the quadrant as the CNC's convention.
Part (Imaginary nose)
With this option, you can manage the toolpaths for inter cycles and rapid motions for:
Roughing and finishing operations programmed with the same tool.
Roughing toolpath in Imaginary Nose, Finishing in Part
We also advise to force the P Point option directly in the tool page, so that you cannot have 2 different piloted points for the same tool.  | ▶️ You can watch a video on Part Imaginary Nose:  |
P point Calculation
The P Point calculation process has been significantly enhanced to improve toolpath efficiency and accuracy. Key improvements include updated dynamic and toolpath simulations, explicit P Point coordinates, elimination of parasite motions, optimized rapid motions, enhanced balanced roughing and finishing, optional inclusion of approach/return points, and a refined gouge check. These advancements result in more efficient, accurate, and reliable toolpaths.
